East African Community Mutual Recognition Procedures(EAC-MRP)
African Medicines Regulatory Harmonization (AMRH)
Regulation of Medicines helps to ensure that patients have access to quality, safe, and efficacious medicines but remains an important but neglected component of promotion and protection of public health because. Investing in the African Medicines Regulatory Harmonization (AMRH) initiative provides an opportunity for strengthening regulatory capacity, cost-effective use of the limited financial and human resources, attainment of the three health-related Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), and promotion of trade and socioeconomic development for African countries and regions.
The objective of the African Medicines Regulatory Harmonization (AMRH) is to ensure that African people have access to essential medical products and other health technologies. AMRH is a programme of the African Union (AU) implemented as part of the Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Plan for Africa (PMPA). Under the theme “Strengthening of Health Systems for Equity and Development in Africa”, the AU Conference of Health Ministers (AUCHM) in April 2007 responded to the AU Assembly Decision 55 (Assembly/AU/Dec.55 (IV) taken during the Abuja Summit in January 2005 which mandated the African Union Commission (AUC) to develop the PMPA within the framework of the NEPAD.
The programme started in 2009 as a response to addressing challenges faced by National Medicine Regulatory Authorities (NMRAs) in Africa. These challenges include; weak or non-coherent legislative frameworks, redundant/duplicative processes, sluggish medicine registration processes and subsequent delayed decision, inefficiency and limited technical capacity, among others. The work of AMRH is guided by three focus areas: policy alignment, regional integration and harmonization, and human and institutional capacity development.
The programme works in collaboration with the AUC, Pan-African Parliament (PAP), World Health Organization (WHO), Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, World Bank (WB), UK Department for International Development (DFID) and US Government-PEPFAR and Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization (GAVI). The AMRH Strategic Plan defines the strategic direction for the medicines harmonization agenda in Africa and provides direction to advance the development of the pharmaceutical sector and provides guidance in monitoring and evaluation.
Mission
Provide leadership in creating an enabling regulatory environment for pharmaceutical sector development in Africa
For more information on African Medicines Regulatory Harmonization follow the link
EAC – MRH) Programme was launched in 2012 becoming the first Regional Economic Community (REC) in Africa to initiate harmonization procedures for medicines regulation under the African Medicines Registration Harmonization Initiative (AMRHI).
The Programme aimed at establishing harmonized and functioning medicines registration and regulation systems within the East African Community (EAC. The Programme is implemented by National Medicines Regulatory Authorities (NMRAs) in all EAC Partner States: The Department of Pharmacy, Medicines and Laboratories (DPML) of Burundi, The National Drug Authority (NDA) of Uganda, Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB) of Kenya, Pharmacy Task Force (PTF) of Rwanda, Drug and Food Control Authority (DFCA) of South Sudan as well as The Tanzania Medicines and Medical Devices Authority (TMDA) and The Zanzibar Food and Drugs Agency (ZFDA) of the United Republic of Tanzania.
African Medicines Regulatory Harmonization (AMRH)
- To implement an agreed upon common technical document for registration of medicines in the EAC Partner States
- To implement a common information management system for medicines registration in each of the EAC Partner States’ NMRAs which are linked in all Partner States and EAC Secretariat
- To implement a quality management system in each of the EAC Partner States’ NMRAs
- To build regional and national capacity to implement medicines registration harmonization in the EAC
- To develop and implement a framework for mutual recognition based on Chapter 21, Article 118 of the East African Community Treaty.
- To create a platform for information sharing on the harmonized medicines registration system to key stakeholders at national and regional level
Achievements of EAC – MRH Programme
- Development of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for Medicine Registration, GMP inspections and Quality Management Systems.
- Common Technical Documents (CTDs) were approved, assimilated and rolled out in all countries.
- Conduct joint assessment activities
- Performed joint GMP inspections

TMDA is the lead NMRA in Medicines Evaluation and Registration (MER)
- Receives dossiers on behalf of Partner States NMRAs
- Coordinates joint assessment in collaboration with EAC Secretariates
- Communicates with Applicants during the evaluation phase
- Maintains the register of medicines registered under the Programme
- Conducts active monitoring of progress of the applications made under the Programme
- Oversees the development and review of guidelines, SOPs and assessment procedures
For more detailed requirements Applicants should refer to the EAC Guidelines on Procedural Aspects for Applications for Marketing Authorization of Pharmaceutical Products. The guidelines can be accessed through our website
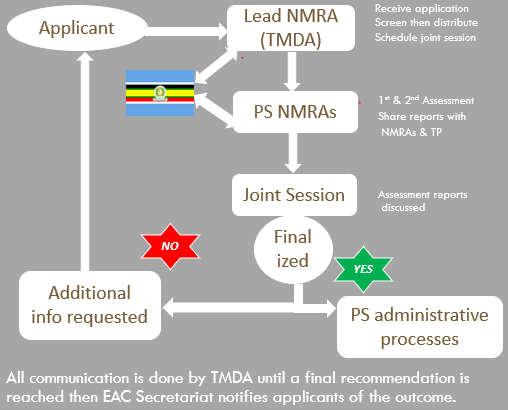
Overview of Joint Assessment Procedure where one application is simultaneously submitted in all EAC Partner States NMRAs so that assessment is done together such that the final results obtained are binding in all Partner States
For the list of products jointly assessed and registered through EAC – MRH Programme click here
| 1. | Cooperation Framework Agreement for EAC Partner States National Medicines Regulatory Authorities. | Download |
| 2. | Lions Head Global Partners. Final Report: Develop a Sustainable Financing Model for National Medicines Regulatory Agencies in the East African Community. | Download |
| 3. | EAC MRH Programme -Joint Regulatory Procedures | Download |

